MPSC राज्यसेवा मुख्य परीक्षा 2023 पोस्ट प्राधान्य & Opting Out वेबलिंक सुरु..! – MPSC State Service Recruitment 2025
MPSC State Services Main Examination 2025 for 457 post
MPSC राज्यसेवा मुख्य परीक्षा 2023 Post Preference & Opting Out वेबलिंक सुरु झाली आहे. Post Preference & Opting Out नोंद करण्याची अंतिम तारीख 18 मार्च 2025 आहे.


After clearing the MPSC 2022 exam, the administration finally issued orders for the appointment of 498 candidates who had succeeded even in the interview. This includes 229 candidates from Group A and 269 from Group B. These candidates had been waiting for appointment for over a year. After Lokmat raised the issue, the chief minister and the administration took immediate cognizance and issued an order for his appointment. The government order was issued on Friday. Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis congratulated the candidates who received the appointments.
एमपीएससी २०२२ च्या परीक्षेत उत्तीर्ण ‘त्या’ ४९८ उमेदवारांना नियुक्ती आदेश
एमपीएससी २०२२ च्या परीक्षेत उत्तीर्ण झाल्यानंतर मुलाखतीतही यशस्वी ठरलेल्या ४९८ उमेदवारांच्या नियुक्तीचे आदेश अखेर प्रशासनाने निर्गमित केले. परीक्षेतील गट ‘अ’च्या २२९ आणि गट ‘ब’च्या २६९ उमेदवारांचा यात समावेश आहे. वर्षभरापासून हे उमेदवार नियुक्तीच्या प्रतीक्षेत होते. ‘लोकमत’ने या विषयाला वाचा फोडल्यानंतर मुख्यमंत्री व प्रशासनाने तातडीने दखल घेत त्यांच्या नियुक्तीचे आदेश काढले. शुक्रवारी शासन निर्णय जारी झाला. मुख्यमंत्री देवेंद्र फडणवीस यांनी ‘एक्स’ वर माहिती देत नियुक्त्या मिळालेल्या उमेदवारांचे अभिनंदन केले.
या संवर्गातील नियुक्त्या – उपजिल्हाधिकारी, तहसीलदार, पोलिस उपअधीक्षक, सहायक पोलिस आयुक्त, सहायक राज्य कर आयुक्त, गटविकास अधिकारी, मुख्याधिकारी, शिक्षणाधिकारी, बालविकास अधिकारी, उपशिक्षणाधिकारी, कक्ष अधिकारी, सहायक प्रादेशिक परिवहन अधिकारी, सहायक गट अधिकारी, सहायक प्रकल्प अधिकारी आदी संवर्गातील पदांच्या नियुक्त्या झाल्या आहेत. राजपत्रित संवर्गाच्या २२९ उमेदवारांना नमूद पदावर २ एप्रिल २०२५ पासून दोन वर्षांच्या प्रशिक्षणासाठी परिविक्षाधीन अधिकारी म्हणून नियुक्ती मिळेल.
MPSC State Services Main Examination 2025 – The Maharashtra Public Service Commission (MPSC) released the interim selection list of 623 candidates for the 2022 examination in March 2024. Subsequently, the court petitions were also disposed of. However, many candidates had been waiting for appointment for over a year. ‘Loksatta’ has raised the issue several times. The state government took note of this and finally released the list of appointments of 623 candidates.
महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोगाच्या राज्यसेवा परीक्षे अखेर ६२३ उमेदवारांना नियुक्ती! ‘एमपीएससी’ची यादी जाहीर

महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोगाच्या (एमपीएससी) २०२२ च्या परीक्षेमधील ६२३ उमेदवारांची मार्च २०२४ मध्ये अंतरिम निवड यादी जाहीर झाली. त्यानंतर न्यायालयीन याचिकाही निकाली निघाल्या. मात्र, अनेक उमेदवार एक वर्षापासून नियुक्तीच्या प्रतीक्षेत होते. ‘लोकसत्ता’ने अनेकदा या विषयाला वाचा फोडली. राज्य शासनाने याची दखल घेत अखेर ६२३ उमेदवारांच्या नियुक्तीची यादी जाहीर केली.
- ‘एमपीएससी’कडून राजपत्रित आणि अराजपत्रित अधिकाऱ्यांच्या विविध पदांसाठी परीक्षा घेतली जाते. परंतु, पूर्व परीक्षा, मुख्य परीक्षा आणि मुलाखत, असा मोठा टप्पा पार करून महत्त्वाच्या पदांवर निवड झालेल्या अधिकाऱ्यांना अनेक वर्षे नियुक्तीची प्रतीक्षा करावी लागते, असे चित्र आहे. ‘एमपीएससी’ने २०२२ मध्ये २३ संवर्गातील ६२३ पदांच्या राज्यसेवा परीक्षेसाठी जाहिरात दिली. मुख्य परीक्षा जानेवारी २०२३ मध्ये तर डिसेंबर २०२३ ते जानेवारी २०२४ या कालावधीत मुलाखती झाल्या.
- १८ जानेवारी २०२४ रोजी गुणवत्ता यादी जाहीर झाली, तर २० मार्च २०२४ रोजी पदनिहाय अंतरिम यादी जाहीर झाली. यात अनेक उमेदवारांना उपजिल्हाधिकारी, तहसीलदार, शिक्षणाधिकारी आदी महत्त्वाच्या पदांवर निवड झाली होती. मात्र, सर्वसाधारण गुणवत्ता यादी जाहीर होताच काही उमेदवार न्यायालयात गेले. त्यामुळे नियुक्त्या रखडल्या होत्या. याचिका निकाली निघाल्यानंतरही आयोगाने अंतिम फेरनिवड यादीही जाहीर केली. मात्र, सामान्य प्रशासन विभागाने या उमेदवारांना नियुक्त्या दिल्या नव्हत्या. मात्र आंदोलनाचा इशाऱ्यानंतर शासनाने उमेदवारांच्या नियुक्तीची यादी जाहीर केली.
MPSC State Service Recruitment 2025 – While thousands of posts are lying vacant in government offices in the state, fewer posts are being filled. The descriptive (written) pattern of mpsc main exam will be implemented from 2025. This will be the last exam in objective format for the preliminary examination and main exam to be held this year. Considering the number of students and vacant posts, the government should increase the seats, otherwise the association will launch an agitation.
आंदोलनाचा इशारा • दोन लाखांवर अर्ज आले, उपविभागीय अधिकारी पदाची भरती नाही
शासकीय विभागात ५६० पदे रिक्त असून पदभरती कमी, कामावर होतोय परिणाम – राज्यात उपशिक्षणाधिकारी पदाच्या ३४७, नायब तहसीलदारांच्या २८१, पोलिस उपायुक्तांच्या १६१ यासह इतर विविध भागातील ५६० प्रमुख जागा रिक्त आहेत. त्या जागा रिक्त असल्याचा परिणाम प्रशासकीय सेवांवर होत आहे. त्यामुळे त्या रिक्त जागा भराव्यात, अन्यथा आंदोलन करण्यात येईल, असा इशारा विद्यार्थ्यांनी दिला आहे.
उपविभागीय अधिकारी अशी अनेक पदे रिक्त आहेत. या परीक्षेस दोन लाखांवर अर्ज आले आहेत. यात खुला वर्ग मुलांसाठी एकूण फक्त ७० पदे आहेत. त्यामुळे राज्य शासनाने विद्यार्थी हिताचा विचार करता मुख्य परीक्षेपूर्वी राज्यसेवा २०२४ च्या जागांमध्ये वाढ करण्यात यावी, अशी मागणी होत आहे.
राज्यात शासकीय विभागात जास्त पदे रिक्त असताना पदभरती मात्र अत्यंत कमी होत आहे. त्यामुळे रिक्त असलेल्या सर्व जागा भरण्याची मागणी विद्यार्थ्यांतून होत आहे. महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोगाकडून एमपीएससीच्या ४३१ जागांसाठी महाराष्ट्र राजपत्रित संयुक्त नागरी सेवा पूर्व परीक्षा २०२४ (राज्यसेवा) नुकतीच घेण्यात आली. वस्तुनिष्ठ स्वरुपात होणारी ही शेवटची मुख्य परीक्षा होती. २०२५ पासून राज्यसेवा परीक्षेत बदल होणार आहेत. ती वर्णनात्मक (लेखी) पद्धतीने होणार आहे. राज्यसेवा २०२४ मध्ये खुल्या वर्गासाठी अत्यंत कमी जागा आहेत.
२०२५ पासून राज्य सेवा परीक्षेत होणार बदल
Vacant Posts details – या रिक्त जागा
- उपजिल्हाधिकारी – १६
- पोलिस उपायुक्त – १६१
- तहसीलदार – ६६
- नायब तहसीलदार – २८१
- मुख्याधिकारी (अ) – ४४
- मुख्याधिकारी (ब) – ७५
- उपशिक्षणाधिकारी – ३४७
वस्तुनिष्ठ स्वरुपातील ही शेवटची परीक्षा – राज्यात शासकीय कार्यालयात हजारो पदे रिक्त असताना कमी प्रमाणात पदे भरली जात आहेत. एमपीएससी मुख्य परीक्षेचा वर्णनात्मक (लेखी) पॅटर्न २०२५ पासूनच लागू केला जाणार आहे. यंदा झालेली पूर्व परीक्षा व होणारी मुख्य परीक्षा वस्तुनिष्ठ स्वरुपातील ही शेवटची परीक्षा असणार आहे. विद्यार्थी संख्या व रिक्त पदाचा विचार करून शासनाने जागा वाढवून द्याव्यात, अन्यथा संघटनेच्यावतीने आंदोलन करण्यात येईल. प्रशांत शिरगूर, राज्य उपाध्यक्ष, स्पर्धा परीक्षा विद्यार्थी असोसिएशन.
जास्त जागा असतानासुद्धा खुल्या प्रवर्गासाठी जागा कमी – जास्त जागा असतानासुद्धा खुल्या प्रवर्गासाठी कमी प्रमाणात जागा उपलब्ध झाल्या. उपजिल्हाधिकारी, तहसीलदार, पोलिस उपअधीक्षक या पदांचा समावेश झालेला नाही. शासनाने राज्यसेवा २०२४ मध्ये जास्त पदांचा समावेश करावा, अन्यथा संविधानिक मार्गाने आंदोलन करावे लागेल. राज लोखंडे, परीक्षार्थी..
MPSC State Service Recruitment 2025 – The State Service Examination, scheduled to be held under the Maharashtra Gazetted Civil Services Preliminary Examination in 2024, is the last examination of objective method and lakhs of students are looking at the exam as the last opportunity for them. Madha MLA Abhijit Patil met the Chief Minister in Mumbai and submitted a memorandum demanding an increase in the number of posts in the Maharashtra State Chartered Civil Services Preliminary Examination for 2024.
राज्य पत्रित नागरी सेवा पूर्व परीक्षा २०२४ साठीची पदसंख्या वाढवावी
मुख्यमंत्र्यांकडे आमदार अभिजित पाटील यांची मागणी – महाराष्ट्र राज्य पत्रित नागरी सेवा पूर्व परीक्षेत २०२४ च्या पदसंख्येत वाढ करण्याची मागणी माढ्याचे आमदार अभिजित पाटील यांनी मुंबईत मुख्यमंत्र्यांना भेटून निवेदनाद्वारे केली. २०२४ मध्ये महाराष्ट्र राजपत्रित नागरी सेवा पूर्व परीक्षेअंतर्गत होणारी राज्यसेवा परीक्षा ही वस्तुनिष्ठ पध्दतीची शेवटची परीक्षा असून, लाखो विद्यार्थी सदरची परीक्षा त्यांच्यासाठी शेवटची संधी म्हणून पाहत आहेत.
- सध्या या राज्यसेवा २०२४ साठी शासनाकडून ४५७ पदांचे मागणीपत्र आयोगाला पाठवण्यात आले आहे. परंतु लाखो विद्यार्थी शेवटची संधी म्हणून प्रयत्न करीत असताना ही पदसंख्या अपुरी आहे. राज्यसेवा २०२२ साठी ६२३ पर्यंत पदसंख्या वाढवून सरकारने विक्रम केला होता. त्याच पध्दतीने राज्यसेवा २०२४ साठीही सर्व विभागांची अतिरिक्त मागणी पत्रे पाठवून पदसंख्येत वाढ व्हावी, अशी स्पर्धा परीक्षा देणाऱ्या विद्यार्थ्यांची मागणी आहे. राज्यसेवा परीक्षेमधील वर्ग-१ व वर्ग-२ या पदांची एकूण ३५ संवर्ग येतात. त्यामधील १६ संवर्गातील एकाही पदाचा समावेश यावर्षीच्या जाहिरातीत नाही.
- सध्या राज्यसेवा परीक्षा २०२५ मध्ये मागणी पत्रे पाठवण्यात यावीत, याबाबत सामान्य प्रशासन विभागाकडून सर्व विभागांना पत्रव्यवहार करण्यात आलेला आहे. परंतु राज्यसेवा २०२४ साठी पुरेशा प्रमाणात मागणी पत्रे पाठवल्याशिवाय २०२५ साठीची प्रक्रिया सुरू करू नये, ही विनंती आहे. त्यामुळे राज्यसेवा २०२५ साठी मागणीपत्रे पाठवण्याच्या प्रक्रियेस तात्पुरती स्थगिती देत पदसंख्या वाढवण्याची मागणी केली.
MPSC Civil Services Combined Preliminary Examination will now be held on August 25 – As per the original advertisement for the Maharashtra Civil Services Gazetted Joint Preliminary Examination-2024, only candidates who have applied from non-reserved (open) or economically weaker section (EWS) are required to submit the option of socially and educationally backward class (SEBC) or other backward class (OBC). The Maharashtra Gazetted Civil Services Combined Preliminary Examination, which was scheduled to be held on July 21, has been postponed. The exam will now be held on August 25.
राज्यसेवा परीक्षा आता 25 ऑगस्टला; शासनाच्या अभिप्रायानुसार ‘EWS’मधील मराठा तरूणांना SEBC, OBCचा पर्याय निवडण्याची संधी; ‘असा’ निवडा विकल्प
परीक्षा आता २५ ऑगस्ट रोजी होणार – महाराष्ट्र नागरी सेवा राजपत्रित संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा-२०२४ परीक्षेसाठी मूळ जाहिरातीस अनुसरून फक्त अराखीव (खुला) अथवा आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकातून (ईडब्ल्यूएस) अर्ज सादर केलेल्या उमेदवारांपैकी ज्या उमेदवारांना सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गाचा (एसईबीसी) अथवा इतर मागासप्रवर्गाचा (ओबीसी) विकल्प सादर करणे आवश्यक ठरते. शासनाच्या अभिप्रयानुसार २१ जुलैला होणारी परीक्षा महाराष्ट्र राजपत्रित नागरी सेवा संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा पुढे ढकलण्यात आली आहे. आता ही परीक्षा २५ ऑगस्ट रोजी होणार आहे.
- महाराष्ट्र नागरी सेवा राजपत्रित संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा-२०२४ साठी सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग अथवा इतर मागासवर्गाचा दावा करण्यासाठी विकल्प सादर करणाऱ्या तसेच नव्याने अर्ज करणाऱ्या उमेदवारांचे जात प्रमाणपत्र हे विकल्प सादर करण्याच्या अंतिम दिनांकापर्यंत म्हणजेच १४ ऑगस्टपर्यंतचे असणे बंधनकारक आहे. दरम्यान, परीक्षेसाठी अर्जाद्वारे अराखीव (खुला) अथवा आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकाचा (ईडब्ल्यूएस) दावा केलेल्या उमेदवाराने सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग अथवा इतर मागासवर्ग आरक्षणातून (ओबीसी) लाभ घेण्यासाठी १५ जुलै ते १४ ऑगस्टपर्यंत विकल्प बदलाची कार्यवाही करावी, असे महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोगाने स्पष्ट केले आहे. राज्य सेवेची २१ जुलैला होणारी परीक्षा आता २५ ऑगस्ट रोजी घेतली जाणार आहे. ‘सकाळ’ने यासंदर्भात वृत्त प्रकाशित केले होते.
- महाराष्ट्र नागरी सेवा राजपत्रित संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षेसाठी ८ मे २०२४ च्या शुद्धीपत्रकानुसार ५२४ रिक्त पदांचा समावेश जाहिरातीत करण्यात आला आहे.सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग किंवा इतर मागासवर्ग विकल्प निवडण्याची मुभा दिलेल्या कालावधीत बऱ्याच उमेदवारांकडे सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग किंवा इतर मागासवर्ग प्रवर्गाचे जात प्रमाणपत्र मिळविण्यास काही अडचणी आल्या असल्याची निवदने प्राप्त झाली होती. त्याअनुषंगाने ज्या उमेदवारांकडे सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्या मागासवर्ग व इतर मागासवर्ग प्रवर्गाचे प्रमाणपत्र नसल्याने त्यांची त्यांच्याकडील आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटक वर्गवारीचे प्रमाणपत्राआधारे त्यांचा मूळ अर्जातील दावा कायम ठेवला आहे.
- अशा उमेदवारांबाबत करावयाच्या कार्यवाहीबाबत शासनाचे अभिप्राय मागविण्यात आले होते. त्यानुसार शासनाने १२ जुलैला (शुक्रवारी) अभिप्रायानुसार महाराष्ट्र राज्यातील सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गीयासाठी आरक्षण अधिनियम-२०२४ ज्या उमेदवारांना सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गाचे जात प्रमाणपत्र उपलब्ध झालेल्या उमेदवारांना आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटक प्रवर्गाचा लाभ अनुज्ञेय नाही. त्यामुळे सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग किंवा इतर मागासवर्ग प्रवर्गातील पात्र उमेदवारांना तसेच इतर कोणत्याही मागास प्रवर्गास आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकाचा विकल्प अनुज्ञेय नाही.
Choose this option… असा विकल्प निवडावा…
- संबंधित उमेदवार आयोगाच्या ऑनलाइन अर्ज प्रणालीतील उमदेवारांच्या प्रोफाइलमधील ‘माय अकाऊंट’ यात परीक्षेच्या जाहिरातीत उपलब्ध करून देण्यात आलेल्या लिंकसमोर दर्शविण्यात आलेल्या ‘क्युशन’ या बटनावर क्लिक विचारण्यात येणारी माहिती भरून विकल्प सादर करावा.
- सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गाचा (एसईबीसी) अथवा इतर मागासवर्गाचा (ओबीसी) दावा करण्यासाठी विकल्प सादर केल्यास संबंधित उमेदवाराचा मूळ अर्जातील अथवा रद्द समजण्यात येईल.
- सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या (एसईबीसी) अथवा इतर मागासवर्गाचा (ओबीसी) विकल्प सादर केलेल्या उमेदवारांना कोणत्याही परिस्थितीत आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकाचा लाभ अनुज्ञेय होणार नाही.
- सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या अथवा इतर मागासवर्गाचे जात प्रमाणपत्र मिळाले आहे. अशा आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकातून दावा केलेल्या उमेदवारांचा आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकातील दावा ग्राह्य धरण्यात येणार नाही. तसेच हा दावा बदलण्याची विनंती भरती प्रक्रियेदरम्यान कोणत्याही टप्प्यात मान्य करण्यात येणार नाही.
- संबंधित परीक्षेसाठी अर्जाद्वारे अराखीव (खुला) अथवा आर्थिकदृष्ट्या दुर्बल घटकाचा दावा केलेल्या उमेदवाराने सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग अथवा इतर मागासवर्ग आरक्षणातून लाभ घेण्यासाठी १५ जुलै ते १४ ऑगस्ट या काळात विकल्प सादर करण्याची कार्यवाही करणे आवश्यक आहे.
- महाराष्ट्र नागरी सेवा राजपत्रित संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षेसाठी सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्ग अथवा इतर मागासवर्गाचा दावा करण्यासाठी विकल्प सादर करणाऱ्या तसेच नव्याने अर्ज सादर करणाऱ्या उमेदवारांचे जात प्रमाणपत्र सदर विकल्प सादर करण्याचा अंतिम दिनांकापर्यंत म्हणजेच १४ ऑगस्टपर्यंतचे असणे आवश्यक आहे.
- या परीक्षेसाठी सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गाचा अथवा इतर मागासवर्गाचा दावा करणाऱ्या उमेदवारांनी सन २०२३-२४ अथवा २०२४-२५ याआर्थिक वर्षात वैध असणारे उन्नत व प्रगत गटात मोडत नसल्याचे प्रमाणपत्र सादर करणे आवश्यक राहील.
MPSC State Service Recruitment 2024 – The Maharashtra Gazetted Civil Services Combined Preliminary Examination of The Maharashtra Public Service Commission (MPSC) will be held on July 6, 2024. As per the revised demand letter received from the government, the revised details of a total of 524 posts in various cadres to be filled through this examination have been given on the commission’s website. On December 29, 2023, an advertisement was released for a total of 274 vacancies. The exam was earlier scheduled to be held on April 28, 2024. However, the exam was later postponed and will now be held on July 6. Kindly Read the details carefully and keep visit us also Keep follow us on What-App Group for fast updates.
MPSC राज्यसेवा परीक्षा 6 जुलै रोजी
महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोगाची महाराष्ट्र राजपत्रित नागरी सेवा संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा 6 जुलै 2024 रोजी आयोजित करण्यात आली आहे. शासनाकडून प्राप्त सुधारित मागणीपत्रानुसार या परीक्षेमधून भरावयाच्या विविध संवर्गातील एकूण 524 पदांचा सुधारित सविस्तर तपशील आयोगाच्या संकेतस्थळावर देण्यात आले असल्याचे आयोगाने कळविले आहे. या परिक्षेसाठी दिनांक 29 डिसेंबर, 2023 रोजी एकूण 274 रिक्त पदांकरीता जाहिरात प्रसिद्ध करण्यात आली होती. या आधी ही परीक्षा दिनांक 28 एप्रिल, 2024 रोजी घेण्याचे नियोजित होते. पण नंतर ही परीक्षा पुढे ढकलण्यात आली आणि आता 6 जुलै रोजी घेण्यात येणार आहे. या भरती संबंधित पुढील सर्व अपडेट्स मिळण्यासाठी govnokriची अधिकृत मोबाईल अँप आपल्या मोबाईल मध्ये डाउनलोड करा. ध्यनवाद..!
- सामाजिक व शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गाकरीता आरक्षण अधिनियम 2024, 26 फेब्रुवारी, 2024 नुसार राज्याच्या नियंत्रणाखालील पदांवरील नियुक्तीकरिता सामाजिक आणि शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गासाठी आरक्षणाची तरतूद विहित करण्यात आली आहे. या अधिनियमातील तरतुदी शासन निर्णय, 27 फेब्रुवारी, 2024 नुसार विषयांकित संवर्गाच्या विज्ञापित जाहिरातीसाठी लागू आहेत.
- प्रस्तुत प्रकरणी सामाजिक व शैक्षणिक शैक्षणिकदृष्ट्या मागासवर्गासाठी आरक्षण निश्चिती करून सुधारित मागणीपत्र पाठविण्याबाबत शासनास कळविण्यात आले. यास्तव, आयोगाच्या दिनांक 21 मार्च, 2024 रोजीच्या प्रसिद्धीपत्रकाद्वारे प्रस्तुत परीक्षा पुढे ढकलण्यात आली असल्याचे जाहीर करण्यात आले होते.
- शासनाकडून प्राप्त सुधारित मागणीपत्रानुसार महाराष्ट्र नागरी सेवा राजपत्रित संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा-2024 या परीक्षेमधून भरावयाच्या विविध संवर्गातील एकूण 524 पदांचा सुधारित तपशील खालीलप्रमाणे आहे.
- अर्ज सादर करण्याचा कालावधीदिनांक 09 मे, 2024 रोजी 14.00 ते दिनांक 24 मे, 2024 रोजी 23:59 पर्यंत आहे.
- ऑनलाईन पद्धतीने विहित परीक्षा शुल्क भरण्याचा अंतिम दिनांक 24 मे, 2024 रोजी 23:59 पर्यंत*
- भारतीय स्टेट बॅंकेमध्ये चलनाद्वारे परीक्षा शुल्क भरण्यासाठी चलनाची प्रत घेण्याचा दिनांक 26 मे, 2024 रोजी 23:59 पर्यंत आहे.
- चलनाद्वारे परीक्षा शुल्क भरण्याचा अंतिम दिनांक 27 मे, 2024 रोजी आहे.
Important Link of MPSC Civil Services Recruitment 2024
Here we give the all essential link for further use.
PDF ADVERTISEMENT– New Advertisement
MPSC State Service Recruitment 2023 : Maharashtra Public Service Commission has issued the notification for the recruitment of ” State Services Main Examination 2023″ Posts. There are total 303 vacancies available for this posts in MPSC State Service Bharti 2023. Job Location for these posts is all over Maharashtra. The Candidates who are eligible for this posts they only apply in MPSC Rajya Seva. All the eligible and interested candidates apply for this post from the given instruction along with the all essential documents and certificates. Applicant apply before the last date. Last date to apply for the the posts is 21st November 2023. Candidates Read the complete details given below on this page regarding the MPSC State Service Recruitment 2023 and keep visit on our website www.govnokri.in for the further updates also you can download our Sarkari Naukri App for the fast updates.
महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोग नि प्रसिद्ध केलेल्या जाहिराती नुसार येथे “राज्य सेवा मुख्य परीक्षा 2023” पदांच्या एकूण 303 रिक्त जागांसाठी अर्ज मागविण्यात येत आहेत. इच्छुक आणि पात्र उमेदवारांनी 21 नोव्हेंबर 2023 या तारखे पर्यंत अर्ज सादर करावे.. तसेच अधिक माहितीसाठी खाली दिलेली लिंक ओपन करावी. सर्व सरकारी जॉब्सची माहिती व्हाट्सअपवर मिळविण्यासाठी आमच्या व्हाट्सअप ग्रुपला जॉईन करा.
MPSC Rajya Seva Bharti 2023 Notification
Here we give the complete details of Maharashtra Public Service Commission Bharti 2023. Educational qualification of posts, Age Limit, Jobs Location, Experience details, how to apply for the posts, where to apply for the posts, last date, important link etc., Candidates go through the complete details before applying the posts. We daily ads the news jobs details on our website telegram channel. So join our Telegram channel for the latest updates.
MPSC Rajya Seva Main Exam Bharti 2023 Details
|
|
| Recruitment Name : | Maharashtra Public Service Commission |
| Number of Vacancies : | 303 Posts |
| Name of Post : | State Services Main Examination |
| Job Location : | All Over Maharashtra |
| Pay-Scale : | As per Group A & Group B Salary matrix |
| Application Mode : | Online Application Form |
| Age Criteria : | 19 to 43 Year |
MPSC Rajya Seva Recruitment 2023 Vacancy Details |
|
| 1. State Services Main Examination 2023 |
303 Posts |
| [better-ads type=’banner’ banner=’109554′ ] | |
MPSC State Service Main Exam 2023- Eligibility Criteria for above posts
|
|
|
Bachelor’s Degree in Commerce with minimum 55% from a Statutory College, OR Passed Final Examination of Chartered Accountant conducted by Institute of Chartered Accountants of India OR Passed Final Examination in Cost Accounting conducted by Institute of Cost and Works Accountants OR Post Graduate Degree in Commerce from a Statutory University, OR Degree (MBA) with specialization in Finance Business Administration from an institution recognized by All India Council of Technical Education. |
Application Fees Details
|
|
|
Rs. 544/- |
|
Rs. 344/- |
How to Apply for MPSC State Service Notification 2023
|
|
|
|
Selection Process in MPSC Rajya Seva Main Exam Notification 2023
|
|
|
|
|
⏰ All Important Dates of MPSC State Service Exam 2023
|
|
| ⏰ Last date to apply : |
21st November 2023 |
Important Link of MPSC Recruitment 2023
|
|
| OFFICIAL WEBSITE | |
| APPLY ONLINE | |
| PDF ADVERTISEMENT | |
|
|
|
MPSC Rajya Seva Name of Posts 2023
- (1)उपजिल्हाधिकारी,गट अ
- (2)पोलीस उपअधीक्षक,गट अ
- (3)सहायक राज्यकर आयुक्त, गट अ
- (4) उपमुख्य कार्यकारी अधिकारी,गट अ
- (5) उपनिबंधक,सहकारी संस्था, गट अ
- (6) शिक्षणाधिकारी, गट अ
- (7) प्रकल्प अधिकारी (आयटीडीपी),गट अ
- (8) तहसीलदार, गट अ
- (9)सहायक गट विकास अधिकारी,गट ब
- (10) उपअधीक्षक,भूमी अभिलेख,गट ब
- (11)सहायक निबंधक,सहकारी संस्था,गट ब
- (12) उपशिक्षणाधिकारी, गट ब
- (13) सहायक प्रकल्प अधिकारी, गट ब
MPSC State Service Exam Syllabus : MPSC Syllabus 2022 has been released by the Maharashtra Public Service Commission (MPSC) on its official website. Candidates can download the latest MPSC Syllabus PDF from the mpsc. gov. in. Along with the notification. Maharashtra Public Service Commission (MPSC) has divided the MPSC syllabus into different stages and papers. The Commission has notified the topics for the prelims and mains. Candidates may check MPSC Rajya Seva Exam Syllabus from the given link.
MPSC Rajya Seva Exam Syllabus
एमपीएससीेने काही दिवसांपूर्वी राज्यसेवेची मुख्य परीक्षा वर्णनात्मक होईल अशी घोषणा करून त्याचे प्रसिद्धपत्रक काढले होते. आता आयोगाकडून राज्यसेवा मुख्य परीक्षेची परीक्षा योजना व अभ्यासक्रमाबाबतचा निर्णय आयोगाच्या संकेतस्थळावर प्रसिद्ध करण्यात आला आहे. तसेच या परीक्षेचा सविस्तर अभ्यासक्रम आयोगाने जाहीर केला आहे.सदर प्रसिद्धीपत्रकाच्या अनुषंगाने राज्यसेवा पूर्व व मुख्य परीक्षेचा इंग्रजी भाषेतील सविस्तर अभ्यासक्रम उमेदवारांच्या माहितीसाठी आयोगाच्या संकेतस्थळावर प्रसिद्ध करण्यात आला आहे.
काही दिवसांपूर्वी महाराष्ट्र लोकसेवा आयोगाने मोठा निर्णय घेतला होता. राज्यसेवा मुख्य परीक्षा वर्णनात्मक म्हणजेच लेखी करण्याचा महत्त्वाचा निर्णय आयोगाने घेतला होता. ही परीक्षा योजना 2023 मधील परीक्षांच्या मुख्य परीक्षेकरिता लागू असेल. तसेच त्यापूर्वी राज्य सेवा पूर्व परीक्षेतील पेपर क्रमांक २ (CSAT) अर्हताकारी केला होता. सदर निर्णयाची अंमलबजावणी दिनांक २१ ऑगस्ट, २०२२ रोजी होणाऱ्या राज्यसेवा पूर्व परीक्षा २०२२ पासून करण्यात येत आहे. तर राज्यसेवा मुख्य परीक्षा वर्णनात्मक पद्धत २०२३ पासून लागू असेल.
CHECK MPSC STATE SERVICE EXAM REVISED SYALLABUS
MPSC Rajyaseva Prelims Syllabus
The MPSC Rajyaseva Prelims will comprise an Online examination. The examination will be conducted for 400 marks and will have multiple-choice questions. In the prelims exam, there are 2 papers. Paper 1 General Studies and Paper 2 CSAT(Common State Aptitude Test). The syllabus for the prelims is given below.
| Paper | Prelims Syllabus |
| Paper I | General Studies
|
| Paper-II | CSAT(Common State Aptitude Test)
|
MPSC Rajyaseva Mains Syllabus
In the mains exam of MPSC Rajyaseva, a total of 6 papers are there. Paper I and II are language papers. Whereas, Paper III, IV, V, and VI are General Studies. Paper I has descriptive questions. Rest all 5 papers are objective-based (MCQs). Check the MPSC Rajyaseva syllabus for the mains exam mentioned in the table below.
| Paper | Mains Syllabus |
| Paper I | Marathi and English
|
| Paper-II | Marathi and English-
|
| Paper-III
General Studies-I |
History
1. Establishment of the British Rule in India: Arrival of the British East India Company, Wars against major Indian powers, Policy of subsidiary alliance, Doctrine of Lapse, Structure of British Raj up to 1857. 2. History of Modern India: Introduction of modern education – Press, Railway, Post and Telegraph, Industries, Land reforms, and Socio-religious reforms and their impact on society. 3. Renaissance Era: a) Social and Cultural Changes – Contacts with Christian Missionaries, Role of English education and the press, Official- social reform measures (1828 to 1857). Socio-religious reform movements: Brahmo Samaj, Prarthana Samaj, Satyashodhak Samaj, Arya Samaj, Ramkrishna Mission, and Theosophical Society. b) Reform movements among the Sikhs and the Muslims, Depressed Classes Mission, Non-Brahmin movement, and Justice Party. 4. Indian Economy under Colonial Rule: The Mercantile phase, The Drain of the Wealth- The Drain Theory of Dadabhai Naoroji, de-industrializationDecline of Indian Handicrafts, Commercialization of Indian Agriculture. Rise of Modern Industry – Role of Indian mercantile communities, Entry of British Finance Capital in India, Tilak’s Swaraj Fund and contribution of G. K. Gokhale. 5. Emergence and growth of Indian Nationalism: Social background, formation of National Associations, Role of Press and Education in social awakening in pre-independent India, Revolt of 1857, the foundation of Indian National Congress, the moderate phase, growth of extremism, Partition of Bengal, Home Rule Movement, Role of important personalities- Surendranath Banerjee, Firozshah Mehta, Dadabhai Naoroji, A. O. Hume, Bipin Chandra Pal, Lala Lajpat Rai, Annie Besant, Aurobindo Ghosh, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Mahatma Gandhi, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru & Others. 6. Famous movements against the British Government: –
7 National movement in Gandhian Era and Dr. B.R. Ambedkars approch to the problem of untouchability:Gandhiji’s leadership and ideology of resistance, Gandhian mass movements, Non- cooperation movement, Civil Disobedience movement, Faizpur Congress session of 1936, Individual Satyagraha, Quit India Movement, Gandhiji and removal of untouchability. Dr. B. R. Ambedkar’s approach to problem of untouchability, Movements for Annihilation of Caste – Dr.Ambedkar’s approach, Gandhiji’s approach, Other Efforts; Unionist Party and Krishak Praja Party, Women’s participation in the National movement. States’ Peoples’ movements. 8. Constitutional Development under British Government: The Indian Council Act-1861, The Indian Council Act-1892, The Indian Council Act-1909 (Morley-Minto reforms), The Government of India Act 1919 (Mont-Ford reforms), The Government of India Act 1935. 9. Growth of Communalism and the Partition of India: Muslim politics and Freedom movement (Sir Syed Ahmed Khan and Aligarh movement, Muslim League and Ali Brothers, Iqbal, Jinnah), Politics of Hindu Mahasabha. 10. Toward the Transfer of Power: The August Offer 1940, The Cripps Mission 1942, The Wavell Plan 1945, The Cabinet Mission Plan 1946, The Mountbatten Plan 1947, The Indian Independence Act 1947 11 India after Independence: Consequences of Partition, Integration of Princely states, Linguistic reorganization of states, Sanyukta Maharashtra movement – Involvement of major political parties and personalities involved therein, Relations with neighbouring countries, India’s role in International Politics : Non- alignment policyNehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri, Indira Gandhi; Progress in Agriculture, Industry, Education, Science and Technology, Emergence of Indira Gandhi’s Leadership, Liberation of Bangladesh, Coalition Governments in States, Students’ unrest, Jayaprakash Narayan and Emergency. Terrorism in Kashmir, Panjab and Assam, Naxalism and Maoism, Environmental Movement, Women’s Movement and Ethnic Movement. 12. Selected Social Reformers of Maharashtra- Their ideology and work: Gopal Ganesh Agarkar, Mahatma Phule, Justice M. G. Ranade, Prabodhankar Thakare, Maharshi Karve, Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj, Maharshi Vitthal Shinde, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar, Lokmanya Tilak, Sarvajanik Kaka Ganesh Vasudeo Joshi, Pandita Ramabai, Dadoba Pandurang Tarkhadkar, Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh, Lokhitwadi Gopal Hari Deshmukh, Justice,K. T. Telang, Dr. Bhau Daji Lad, Acharya Balshastri Jambhekar, Jagannath Shankarsheth, Gopal Krishna, Gokhale, Kalkarte Shivram Mahadeo Paranjape, Vishnushastri Chiplunkar, D. K. Karve, R. D. Karve, VinobaBhave, Vinayak D. Sawarkar, Annabhau Sathe, Krantiveer Nana Patil, Lahuji Salve, Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil, Vishnubuva Brahmachari, Senapati Bapat, Rashtrasant Tukadoji Maharaj, Baba Amte, Sant Gadge Baba. 13. Cultural Heritage of Maharashtra (Ancient to Modern): Kanheri, Elephanta, Ajanta, Ellora caves, Lonar lake, Forts, etc. Performing Arts – Dance, Drama, Films, Music, Folk Arts – Lavani, Tamasha, Povada, Bharud, and other folk dances,Visual Arts -Architecture, Painting and Sculpture. Festivals. Impact of Literature and Saint literature on socio-psychological development of Maharashtra: Bhakti, Dalit, Urban and Rural Literature. Geography- With special reference to Maharashtra
Interior of the Earth. Composition and physical conditions. Indogenic and Exogenic Forces, Rocks and Minerals. Controlling factors on Evolution of the Landforms. Concept of the Geomorphic cycles. Landforms associated with Fluvial, Desert, Glacial and Coastal Regions. Evolution and Geomorphology of the Indian Sub-Continent. Major Physiographic Divisions of the India. Physiography and the geomorphic features of the Maharashtra State. Natural Landscapes in Maharashtra- Hills, Ridges, Table lands, Spot holes. Water falls. Hotsprings and Beaches.
School of thoughts in Human Geography. Determinism and Possibilism, Stop and Go Determinism, Different approaches to achieve Development. Human settlements: Rural Urban settlements- site, situation, Types, size, spacing and Morphology. Major Problems of Rural and Urban Settlements. Rural-Urban Fringe, Urbanisation : Process of Urbanisation, sphere of urban influence, Regional imbalances.
Sources of population data. Growth, Density and Distribution of the population in Maharashtra. Population Structure and characteristics. Components of population change- Fertility, Mortality and Migration. Levels and Trends of-fertility, mortality and migration in Maharashtra. Population Growth and Economic Development, Population policies.
Ecosystem – Components: Biotic and Abiotic. The flow of Energy, Energy Pyramid. Nutrient cycling. Food chain and Food web. Environmental degradation and conservation. Global Ecological Imbalances. Reduction in Biodiversity. Threats of biodiversity, Man-Wild Life conflicts. Depletion of forests. Global warming- Green House Effects- The Role of CO, CO2, CH4, CFC’s , Nitrogen- oxides (NO). Acid Rains. Heat Islands in Maharashtra. Environmental Laws and Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). Kyoto Protocol and Carbon Credits.
The Term of Aero (sky) and space. GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing. The Era of Space Technology in relation to – Defence, Banking, Internet, Telecommunication. Planning in Transportation. (Railways, Roads, Navy and Air transportation.) Health and Education. Mission Shakti in India. Anti Satellite Mission. Satellite Space Assets. The Role of ISRO and DRDO in the Research and Development of space Technology. The Management of Space Garbage, Prevention of Arm Race in Space. Geo-Strategic position of India. a. Fundamental of Remote sensing:
b. Aerial Photographs :
c. GIS and its applications :
Agriculture
|
| General Science Paper-II | Indian constitution and Indian politics (with special reference to Maharashtra) and law
1.The Constitution of India:
2. a) Indian Federalism
b) Indian Political System (Structure, Powers and Functions of Governments) Nature of Indian FederationUnion & State – Legislature, Executive & Judiciary, centre-state Relations- Administrative, Executive & financial; Relations, statutory Powers, Allocation of subject
3. Evolution of Indian Administration: a. Pre-British Period b. British Period c. After Independence Period 4. State Government and Administration ( With Special Reference to Maharashtra) : a. Formation and Reorganization of Maharashtra State b. Governor, Chief Minister, Council of Ministers c. State Secretariat, Chief Secretary-Functions and Role d. Legislature- Legislative Assembly, Legislative Council- Powers and Function 5. Rural and Urban Local Government and Administration: Attributes of Local Government
6. District Administration:
7. Political Parties and Pressure Groups:
8. The Electoral Process
9. Mass Media:
10. Education System:
11. Administrative Law: Rule of law. Separation of powers, Delegated legislation, Administrative Discretion, Administrative Tribunals, Principles of Natural Justice, Vigilance Commission, Lokpal & Lokayukta, Constitutional protection to public servants. 12. Maharashtra Land Revenue Code 1966: Definitions, Classes & kinds of Lands, Use of Lands & procedure of change of use, Assessment of land revenue, Land Records, Provisions for appeal, Revision & Review. 13. Some Pertinent Laws:
14 Social Welfare and Social Legislation: Constitutional provisions relating to socio-economic justice, Protection to Women under: The Constitution of India & Human Rights, The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act 2005, Protection to Child under Constitution and Human Rights, Concept of free legal aid & Public Interest Litigation. 15 Financial Administration:
16 Agricultural Administration and Rural Economy:
17 Public Services:
18. Constitutional and Statutory Bodies:
19. Concepts, Approaches, and Theories in Public Administration:
20. Public Policy:
|
| General studies –III | Human resource development (HRD) and human rights:
1. HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT: a. Human Resource Development in India – Present Dimensions of Population in India – Quantitative aspect (Size, Growth, Growth Rate, Age, Sex, Rural and Urban population, Birth Rate, Mortality Rate) Qualitative aspect (Education, Healthcare, Human Development, Index, Population policy, population explosion, population projection upto 2050, Importance and need of Human Resource Planning in modern society, components and factors involved in planning of Human Resources, Nature, Types and problems of unemployment in India, Trends in employment in India, Demand estimate of skilled manpower in different sectors and areas, government’s policy and schemes to reduce unemployment. Institutions engaged in development of human resource and field of education – UGC, AICTE, NCTE, RUSA, ITIs, NCVT, IMC, NCERT, NIEA, IIT, IIM) b. Education: Education as a tool of HR development and social change. Education (Pre-primary to Higher Education) system in India. Problems and issues (Universalisation of education, vocationalisation of education, Quality improvement, Dropout rate etc.) Education for Girls, Socially and Economically underprivileged classes, Handicapped, Minorities, Talent Search etc. Govt. policies, Schemes and programms for Education. Govt. and Voluntary Agencies involved in promoting, regulating and monitoring Formal, Non-formal and Adult education. E-Learning. Impact of globalisation and privatisation on Indian education. National Knowledge Commission, National Commission for Higher Education and Research, IITs, IIMs, NITs, Right to Education-2009, NEP-2019 as updated c. Vocational Education: As a tool of HR development. Vocational/ Technical Education- Present status, systems and training in India particularly in Maharashtra. Govt. policies, schemes and programs – Problems, issues and efforts to overcome them. Institutes involved in promoting, regulating, accrediting vocational and Technical Education. NSDC (National Skill development Corporation)
d.Health – World Health Organisation (WHO) Objective, Structure, Functions and Programmes , Health policy of India, various schemes and programme, health care system in India, Vital Statistics of Health in India, problems and issues related to health care (Malnutrition, Maternal Mortality Ratio, etc.) Janani-Bal Suraksha Yojana, National Rural Health Mission, Pradhanmantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY) e. Rural Development – Empowerment of Panchayat Raj System, role of Gram-panchayat in rural development, land reforms and development, Schemes and programmes of agriculture and farmer welfare, role of cooperative institutes in rural development, financial institutes involved in rural development (Self Help Group-(SHG), Micro-finance) rural employment schemes, rural water supply programme and sanitation programme, infrastructure development e.g. energy, transportation, housing and communication in rural area, national rural employment guarantee schemes (NREGS), Mission Antodaya, Gram Swaraj Abhiyan 2. HUMAN RIGHTS:
International human rights standards, its reflection in the Indian Constitution, mechanism to enforce and protect Human Rights in India. Human Rights Movement in India. Problems related to human rights deprivations such as poverty, illiteracy, unemployment, social-culturalreligious practices, violence, corruption, terrorism, exploitation of labour, custodial crimes etc. Need for training and practice of human rights and human dignity in a democratic set up. Globalisation and its impact on different sections of Indian Society. Human Development Index, Infant Mortality Rate, Sex Ratio.
Problems and issues (Infant mortality, malnutrition, child labour, children education etc.) government policies, welfare schemes and programmes –Role of international agencies, voluntary organizations, NGOs, community resources. Child labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act, Protection of Children from Sexual Offence Act, Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
Problems and issues of Women (Gender inequality, violence against women, Sex ratio, Female infanticide, Female foeticide, etc.) Government policy, schemes and programmes for women development, Welfare and Empowerment, Role of international agencies, voluntary organizations and community resources. Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA)
Problems and issues (unemployment, unrest, drug addiction etc), Government policy – development schemes and programme, Role of international agencies, voluntary organization and community resources. National Policy on Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, National Youth Policy.
Problems and issues (Malnutrition, Integration and development etc) Tribal welfare- government policy, welfare schemes and programmes, Role of international agencies, voluntary organizations and community resources.Forest Rights Act .
Problems and issues (inequality in opportunity etc.) – Government Policy, welfare schemes and development programs – Role of international agencies, Voluntary Organisations and Resource mobilisation and Community participation.
Problems and issues – Government Policy – welfare schemes and programs – Role of international agencies, Voluntary Organisations and Community participation for their development. Utilization of their services in developmental activities.
Problems and issues (working conditions, wages, health and problems related to organised and unorganised sectors) – Government Policy, welfare schemes and programs – Role of international agencies, community and Voluntary Organisations.
Problems and issues (inequality in educational and employment opportunity etc.) -Government Policy, welfare schemes and programs – Role of international agencies, Voluntary Organisations in employment and rehabilitation.
(People affected by Development projects and Natural Calamities.) – Strategy and programs – Legal Provisions – Consideration of different aspects like economic, cultural, social, psychological etc.
United Nations and its specialised agencies – UNCTAD, UNDP, ICJ, ILO, UNICEF, UNESCO, UNCHR/ UNHRC, APEC, ASEAN, OPEC, OAU, SAARC, NAM, Commonwealth of Nations, European Union, SAFTA, NAFTA, BRICS, RCEP
Definitions, Objects, Salient features of the existing act- Rights of consumers, Consumer disputes and redressal machinery, Different kinds of Forums- Jurisdiction, Powers, functions, procedures and Appeals.
Fostering of social norms, Socialisation, values and ethics through formal and informal agencies such as Family, Religion, Education, Media etc. |
| General studies –IV | Economy and planning, the economics of development and agriculture, science and technology development.
a. MACRO-ECONOMICS 1. Macro Economics: National Income concepts- GDP,GNP, GVA, At factor cost, At market price, GDP deflator, Methods of national income accounting, National Income Accounting in India, National Income accounting problems in India, Business cycles, Employment concepts- measures of unemployment. 2. Growth & Development:
3. Public Finance: Role of public finance in market economy (Market failure & Development oriented)- Criteria for public investment. Merit goods and public goods, Sources of revenue- incidence and effect, Types of public expenditure, budget deficits, Fiscal Deficits – Concepts, Control of Deficits, Public debt, Performance, Based Budgeting and Zero Based Budgeting, Gender based budgeting. 4. Money: Functions of money- base money– high-powered money- quantity theory of money – money multiplier. Monetary and non-monetary theories of inflation – control of inflation: monetary, fiscal and direct measures 5. International Trade and International Capital: International trade as an engine of growth- theories of international trade- Classical & modern theories, Role of foreign capital and technology in growth – multi-national corporations .International Financing Agencies– IMF, World Bank, IDA & ADB, Regional Trade Agreements – SAARC, ASEAN, WTO and International Trade & Investments, TRIPs & TRIMs. b. INDIAN ECONOMY 1. Indian Economy- Overview:
2. Indian Agriculture & Rural Development:
3. Co-operation: Concept, Meaning, Objectives, new principles of co-operation. Growth and diversification of co-operative movement in India & Maharashtra, Self Help Groups. State policy and Co-operative sector- Legislation, Supervision, Audit and Aid. Problems of Co-operatives in Maharashtra. Prospects of Cooperatives in the era of global competition. 4. Monetary & Financial Sector: Indian financial system- structure, Role of RBI, Monetary & Credit Policy, Transmission mechanism, Inflation targeting in India, Growth in banking & non- banking financial institutions in India, Money market- developments post-1991, Capital market- developments post-1991, Role of SEBI, Financial sector reforms 5. Public Finance and Financial Institutions: Sources of revenue (Central & State), Public Expenditure (Centre and States)- Growth and causes. Public Expenditure Reform – Review of Tax Reforms- VAT, GST. Central & State deficits & deficit financing, Public debt- Growth, Composition and Burden. Problem of States’ Indebtedness to Centre. Finance Commissions in India, Fiscal Reforms in India 6. Industry and Services Sector: Importance and role of industries in economic and social development, Growth Pattern, Structure of Largescale Industries in India with special reference to Maharashtra. MSMEs- Growth, problems, prospects & policies, SEZs, SPVs. Industrial sickness- measures, Industrial exit policy Industrial policies- pre & post-1991, India & Ease of doing business, Composition and growth of services sector in India. Indian labour- issues, measures & reforms, Social security measures 7. Infrastructure Development: Types of infrastructure, Growth of infrastructure such as Energy, Water supply and sanitation, Housing, Transport (Road, Ports etc.), Communications (Post and Telegraphs, Telecommunication), Network of Radio,TV, Internet.Problems related to Infrastructure in India. Infrastructure financing- challenges & policy alternatives- Public-Private Sector Partnership (PPP). FDI and Infrastructure Development, Privatisation of infrastructure development. Centre and State Government Policies for Infrastructure Development- SPVs., Affordable housing, slum rehabilitation 8. International Trade & Capital: Growth, Composition and Direction of India’s Foreign Trade. Foreign trade policy – Export Promotion initiatives. Foreign Capital flows- Composition and Growth- FPI, FDI. E-Commerce, external commercial borrowings. Role of Multinationals. International Credit Rating institutions & India. Exchange rate management in India 9. Economy of Maharashtra: Salient features of agriculture, industry and service sectors, GoM policies for agriculture, industry and service sectors, drought management in Maharashtra – FDI in Maharashtra, Maharashtra in comparison with rest of India. 10. Agriculture:
Causes of low productivity – Contribution of Agriculture to the National income and employment. Basic Agricultural inputs, farm size and productivity, Govt. Policies towards doubling farmers income. Other Government policies, schemes and programmes for agriculture production and developments such as land reforms and land utilisation, soil and water conservation, rainfed farming, Irrigation and its methods, Mechanization of Agriculture. General price index, inflation and deflation. GST and agricultural taxation. Present Status and prospects of international trade agreements in Agriculture (WTO etc.) Different Crop Insurance Schemes in India, Role of ICAR, MCAER.
11. Food and Nutrition: Trends in food production and consumption in India, Self-sufficiency in food, Problem of food security, Problems and issues of food spoilage, storage, procurement, distribution, import and export of food. Common nutritional problems in India. Government Policies, schemes, programs such as PDS, Food for work, Mid-day Meal Scheme, and other nutritional programs. Green revolution and its impact on food self-sufficiency. Oil for food programme, Nutritional security. National food security Act 2013. 3. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS a. Energy Science:
b. Computer and Information Technology
c. Space Science and Technology: Indian space policies and programmes, space missions, ISRO, Introduction , working principle, and applications of Indian Artificial satellites viz. Television, broadcasting, Telecommunication, Weather forecasting, GPS, disaster forecasting, Education. Satellite launch vehicles, Space debris.
4. BIO- TECHNOLOGY
5. India’s Nuclear Programme: Introduction, necessity, salient features, Recent Nuclear Policies, Nuclear Tests, Nuclear Thermal power generation- principle, construction, working and environment. Nuclear waste, nuclear accidents etc. Nuclear power plants in India- Use of nuclear technology like consumer products, food and agriculture, medicines etc. 6. Disaster Management- (Special reference to Maharashtra) Definitions, Environmental Stress, Classification of Disaster.
Identification and Distribution of Hazards. Zonation and Risk Analysis. Awareness of Hazards. Pre-hazard conditions. Rescue operations. Reclamation |
MPSC State Service Bharti 2023: The Public Service Commission has taken an important decision to change the format of the examination, Changes have been made in the examination system of MPSC State Public Service Commission. This decision will be implemented from the pre-examination to be held on 21st August. At the same time, the most important change has been made in the main examination. Read more details as given below.
MPSC राज्य लोकसेवा आयोगाच्या परीक्षा पद्धतीत बदल
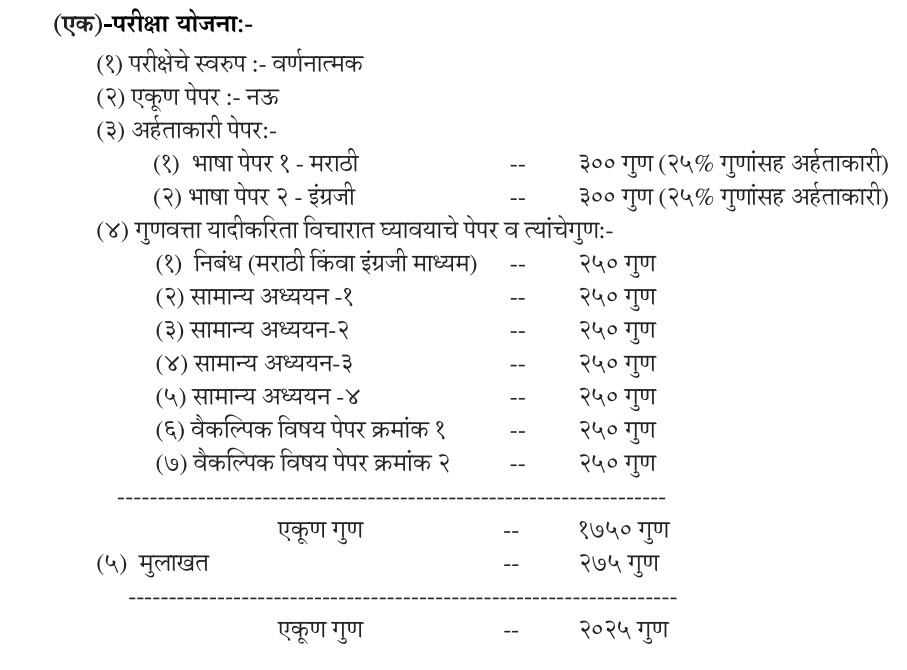
राज्य लोकसेवा आयोग (एमपीएससी)ने परीक्षा पद्धतीमध्ये अमुलाग्र बदल करत परीक्षेचा दर्जा केंद्रीय लोकसेवा आयोगाच्या परीक्षेशी समकक्ष केला आहे. यानुसार आता मुख्य परीक्षा १७५० गुणांची होणार आहे.
राज्यसेवा पूर्व परीक्षेतील पेपर क्रमांक दोनबाबत अनेक उमदेवारांनी नाराजी व्यक्त केली होती. यानुसार यावर अभ्यास करण्यासाठी सेवानिवृत्त सनदी अधिकारी चंद्रकांत दळवी, धनंजय कमलाकर आणि माजी कुलगुरू एस. एफ. पाटील यांची समिती नेमण्यात आली होती.
या समितीच्या शिफारशींनुसार राज्य लोकसेवा आयोगाने परीक्षेच्या स्वरुपात बदल करण्याचा महत्वपूर्ण निर्णय घेतला आहे. याबाबतचे प्रसिद्धपत्रक शुक्रवारी प्रसिद्ध करण्यात आले. यानुसार पूर्व परीक्षेतील पेपर क्रमांक २ (सीसॅट) आर्हताकारी करण्यासाठी २ मे रोजी प्रसिद्ध केलेल्या परिपत्रकानुसार किमान ३३ टक्के गुणांची अट निश्चित करण्यात आली आहे.
हा निर्णय येत्या २१ ऑगस्ट रोजी होणाऱ्या पूर्व परीक्षेपासून लागू करण्यात येणार आहे. याचबरोबर सर्वात महत्त्वाचा बदल मुख्य परीक्षेत करण्यात आला आहे. हा बदल करताना ही परीक्षा केंद्रीय लोकसेवा आयोगाशी समकक्ष करण्यात आली आहे. सध्या मुख्य परीक्षा ७०० गुणांची होते आणि १०० गुणांची मुलाखत घेण्यात येते. मात्र आता ही मुख्य परीक्षा १७५० गुणांची होणार आहे. तर २७५ गुणांची मुलाखत घेण्यात येणार आहे. अशाप्रकारे एकूण २०२५ पैकी गुण देण्यात येणार आहेत. यामध्ये एकूण नऊ पेपर होणार आहेत. ही संपूर्ण परीक्षा वर्णनात्मक स्वरुपाची असणार आहे.
यामध्ये भाषा पेपर १ मराठी आणि भाषा पेपर २ इंग्रजीचा प्रत्येकी ३०० गुणांचा होणार असून यामध्ये प्रत्येकी २५ टक्के गुणांची आर्हता निश्चित करण्यात आली आहे. याशिवाय अन्य सात पेपर असतील यामध्ये दोन्ही माध्यमाच्या निबंधासाठी २५० गुणांचा पेपर, सामान्य अध्ययनाचे चार पेपर आणि दोन वैकल्पिक विषयांच्या पेपरचा समावेश असणार आहे. सामान्य अध्ययन १, सामान्य अध्ययन २ व सामान्य अध्ययन ३ या पेपरमध्ये आंतरराष्ट्रीय, राष्ट्रीय व महाराष्ट्राशी संबंधित विषयांचा अभ्यासक्रमांचा समावेश राहील. तर सामान्य अध्ययन-४ हा पेपर उमेदवारांसाठी नैतिकता, चारित्र्य व योग्यता या विषयावर राहील असेही आयोगाने स्पष्ट केले आहे.
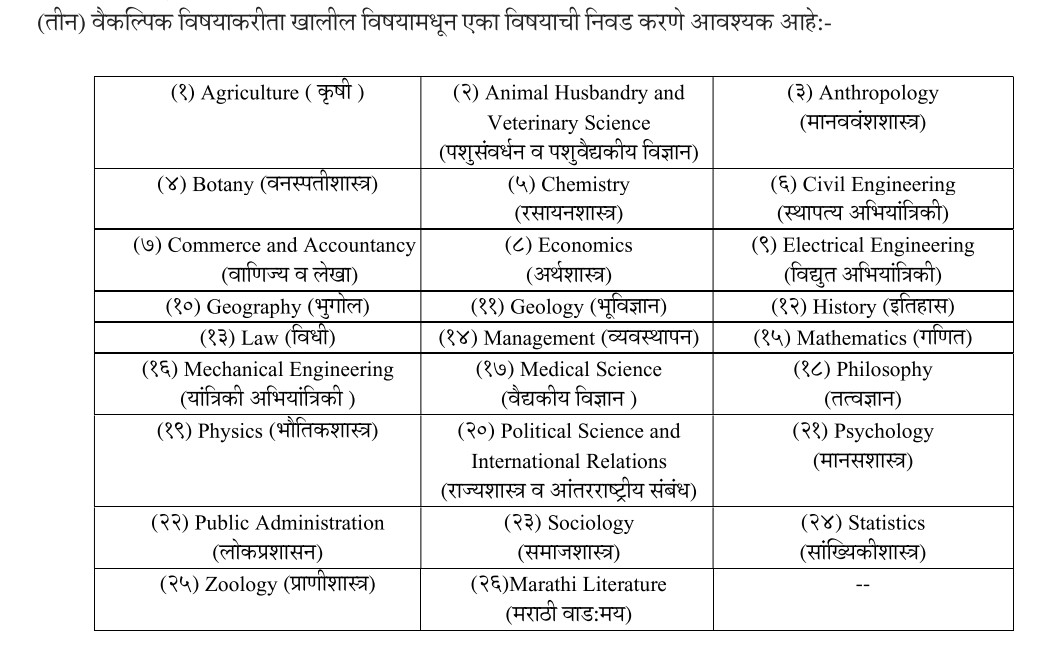
वैकल्पिक विषयांसाठी २६ विषयांचे पर्याय विद्यार्थ्यांना देण्यात आले आहे. राज्यसेवा मुख्य परीक्षेकरीता हे बदल मुख्य परीक्षा २०२३पासून लागू करण्यात येईल असे आयोगाच्या सचिवांनी स्पष्ट केले.
MPSC New Exam Plan
अशी आहे नवी परीक्षा योजना
परीक्षेचे स्वरुप : वर्णनात्मक
- एकूण पेपर – नऊ
अर्हताकारी पेपर
- १. भाषा पेपर १ – मराठी – ३०० गुण
- २. भाषा पेपर २ – इंग्रजी – ३०० गुण
गुणवत्ता यादीकरीता विचारात घ्यावयाचे पेपर
- १. निबंध (मराठी किंवा इंग्रजी माध्यम) – २५० गुण
- २. सामान्य अध्ययन – १ – २५० गुण
- ३. सामान्य अध्ययन – २ – २५० गुण
- ४. सामान्य अध्ययन – ३ – २५० गुण
- ५. सामान्य अध्ययन – ४ – २५० गुण
- ६. वैकल्पिक विषय पेपर क्रमांक १ – २५० गुण
- ७. वैकल्पिक विषय पेपर क्रमांक २ – २५० गुण
एकूण गुण – १७५०, मुलाखत – २७५ गुण, एकूण गुण – २०२५




MPSC State Services Main Examination 2023 for 303 post